Gate Research: Ten Years of ETH: From World Computer to Global Settlement Layer
The report also reviews representative ecosystem projects and innovation cases—including DeFi, NFTs, stablecoins, and cross-chain protocols—demonstrating how Ethereum’s technical upgrades and application deployment have been closely intertwined. Over ten years, this process has formed an evolutionary loop of “demand-driven growth → innovation → standardization → economic optimization → sustainable development.”Introduction
In 2013, Vitalik Buterin proposed a new idea within the Bitcoin community: if blockchain could be used not only for transaction records but also for running arbitrarily complex programs, it could become a true “world computer.” This vision gave birth to Ethereum, which officially launched in 2015. Unlike Bitcoin, which emphasizes “peer-to-peer electronic cash,” Ethereum introduced smart contracts and a Turing-complete virtual machine (EVM), providing a brand-new foundational infrastructure for the development of decentralized applications.
Over the past decade, Ethereum has gone through a unique path of evolution — from the release of the genesis block, to facing security challenges and community splits, and later multiple system upgrades and a transition in its consensus mechanism. Today, it is not only the most active smart contract platform but also the technological backbone for emerging industries such as decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), and blockchain-based gaming (GameFi).
From a technical perspective, Ethereum stands as the most representative example in the public blockchain field. It has led the shift from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake and pioneered the practical adoption of frontier technologies such as zero-knowledge proofs, rollups, and account abstraction. From an economic standpoint, Ethereum’s native asset, ETH, has evolved from being merely a “gas token” into a core digital asset that serves settlement, staking, and value storage functions. On the industry level, the prosperity of the Ethereum ecosystem has laid the foundation for the blockchain sector and fueled decentralized experiments across finance, art, gaming, and beyond.
This report aims to review the core technical upgrades of Ethereum at different stages, analyze the driving forces behind them, explore how these upgrades have shaped its ecosystem and industry landscape, and forecast the future technological trajectory of Ethereum.
The Birth of Ethereum (2013–2015)
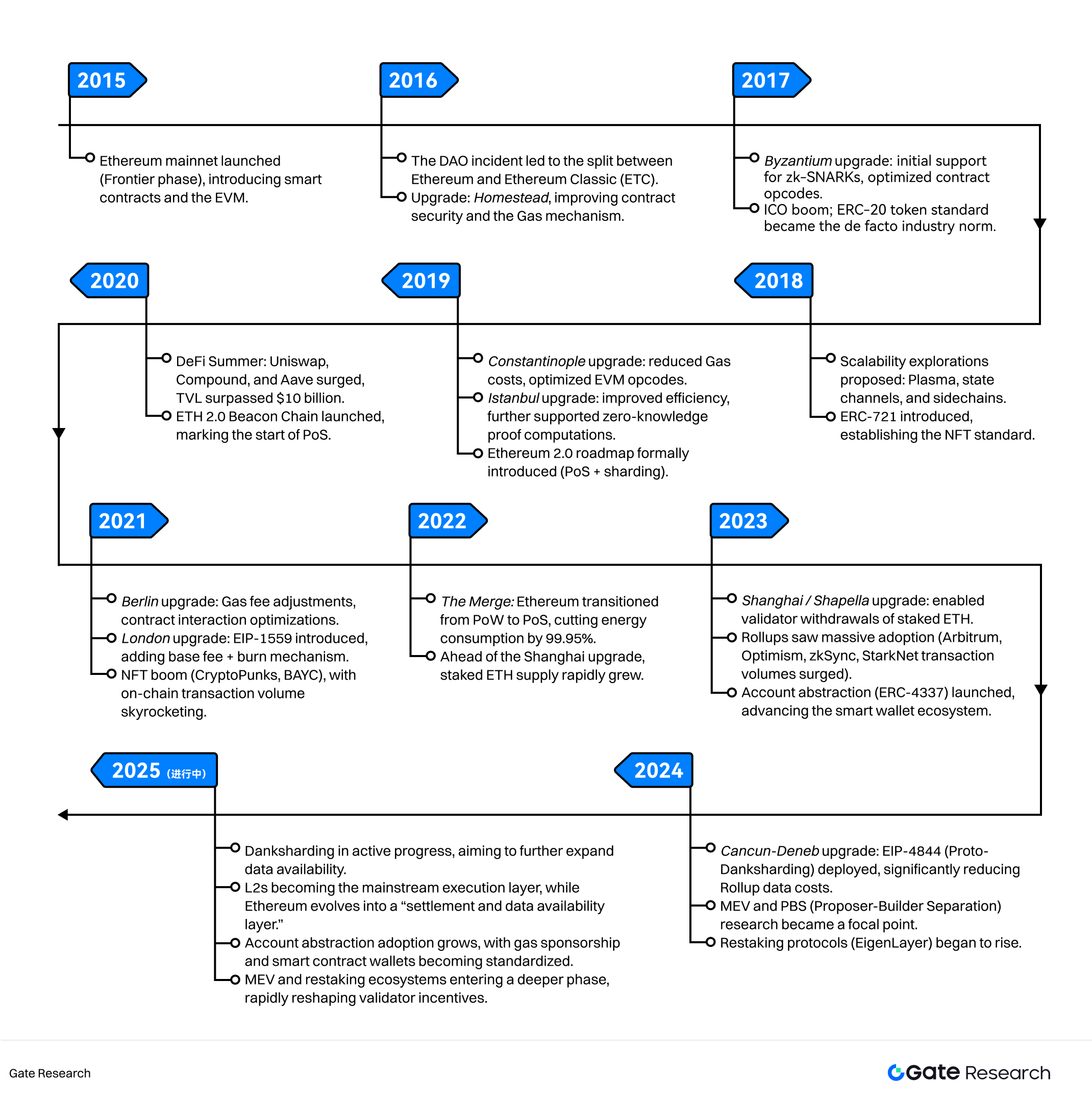
By 2013, Bitcoin had gradually gained global attention, but its functionality remained limited to value transfer. During his active participation in the Bitcoin community, Vitalik Buterin keenly recognized that although Bitcoin scripts offered a degree of programmability, they lacked generality and could not support complex applications. In his white paper published on November 27, 2013, he proposed that if a blockchain platform could run a Turing-complete virtual machine, developers would be able to deploy programs with arbitrary logic on-chain. This idea opened up new possibilities for decentralized applications and directly shaped Ethereum’s technological vision: a globally shared, tamper-proof “world computer.”
In 2014, the Ethereum team conducted a token presale to raise funds for the project, allowing participants to purchase ETH with Bitcoin. The presale not only provided the capital necessary for early-stage development but also fostered a sense of consensus and participation within the community. Around the same time, the Ethereum Foundation was established in Switzerland, providing institutional support for governance and technological research.
On July 30, 2015, Ethereum’s genesis block was launched, marking the birth of Ethereum 1.0. Its design rested on three key pillars. First, the introduction of smart contracts and the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) enabled developers to write self-executing programs in languages such as Solidity, making decentralized application deployment possible. Second, the gas mechanism was introduced: every transaction or smart contract execution required gas, a unit for measuring computational and storage costs. This mechanism ensured rational allocation of network resources while forming the foundation of Ethereum’s economic model. Third, its open and flexible architecture laid the groundwork for the emergence of standardized protocols such as ERC-20 and ERC-721.
In its early phase, the Ethereum ecosystem remained immature—application numbers were limited, and network performance was far from optimized. Compared with Bitcoin’s positioning as “digital gold,” Ethereum functioned more as an experimental platform for decentralized applications.
Security Challenges and Governance Experiments (2016)
The year 2016 is widely regarded as the first major test in Ethereum’s history. At that time, the Ethereum mainnet had been live for less than a year, and the ecosystem was still in its exploratory phase. Yet it was in this year that the DAO incident not only exposed the fragility of smart contract security but also forced the Ethereum community to make a crucial choice amid shocks to its governance model and value alignment.
The DAO (The Decentralized Autonomous Organization), initially launched by the Slock.it team, was envisioned as a decentralized venture capital fund built on Ethereum, allowing token holders to collectively decide investment directions through voting. The DAO began its crowdfunding campaign in May 2016 and, within just 28 days, attracted over 11.5 million ETH—worth around $150 million at the time, representing about 14% of Ethereum’s circulating supply.
However, on June 17, 2016, an attacker exploited a reentrancy bug in the DAO contract code. By repeatedly calling the withdrawal function before the balance update was triggered, the attacker siphoned off funds in a recursive loop. In total, approximately 3.6 million ETH—worth about $50 million at the time—was drained. The incident shocked the entire cryptocurrency community and cast serious doubts on Ethereum’s security.
Market data underscored the impact. Following the DAO hack, Ethereum’s price fell from above $20 to below $13 within days, wiping out nearly 40% of its market capitalization. By contrast, Bitcoin’s price remained relatively stable, highlighting the market’s heightened sensitivity to Ethereum’s security risks. Meanwhile, DAO token holders and the broader Ethereum community became embroiled in an intense debate over how to respond.
Three major positions emerged:
- Status Quo: Uphold the principle of “code is law,” respecting the immutability of on-chain actions.
- Soft Fork: Freeze the attacker’s stolen funds, though this failed to address underlying security flaws.
- Hard Fork: Implement a protocol upgrade to move the stolen funds into a refund contract, allowing investors to reclaim their ETH.
After weeks of heated debate and multiple rounds of voting, the community ultimately opted for the hard fork, which was executed on July 20, 2016. On the forked chain, the stolen funds were redirected into a refund contract, enabling investors to recover their ETH. However, some members who adhered to the principle of immutability rejected the fork and continued maintaining the original chain, giving rise to Ethereum Classic (ETC). From then on, the Ethereum community split into two chains—ETH and ETC—making this governance dispute one of the most iconic hard fork cases in blockchain history.
The market consequences were also significant. In the weeks following the fork, ETH’s price gradually recovered, reaching the $8–10 range by the end of 2016. Meanwhile, ETC secured a short-term market capitalization of several hundred million dollars and developed its own independent community. Yet, over the long term, ETH quickly outpaced ETC in developer activity, application growth, and capital inflows. According to Electric Capital’s developer report, by 2017 ETH had over 250 monthly active developers, compared with fewer than 30 for ETC, with the gap widening rapidly.
The significance of the DAO incident went far beyond price swings and community division. It directly shaped Ethereum’s subsequent trajectory. On one hand, developers and investors began to place far greater emphasis on smart contract security, fueling the rapid rise of the blockchain security auditing industry. On the other hand, the clash of governance philosophies sparked a long-running debate between “code is law” and “community consensus first.” Ethereum’s choice of the latter gained it broader mainstream adoption from both capital and users, though it also foreshadowed future governance challenges.
The DAO hack of 2016 was a high-stakes trial that ultimately validated Ethereum’s resilience. Although millions of ETH were stolen, through governance action and community consensus Ethereum not only avoided a prolonged trust crisis but also developed its governance mechanisms and security culture. This experience laid a crucial institutional foundation for the platform’s later explorations in scalability and technological upgrades.
Key Stages of Technological Evolution
Throughout Ethereum’s ten-year journey, each major technical upgrade has represented not only a milestone for the industry but also a profound experiment in blockchain infrastructure. From early scalability explorations, to the transition to Proof of Stake (PoS), and later to rollups and data availability enhancements, every stage has involved specific proposals and implementation pathways. This chapter dissects these pivotal stages, focusing on their core mechanisms and industrial impact.
4.1 Scalability and Standardization Exploration (2017–2019)
The ICO boom of 2017 exposed Ethereum’s fundamental throughput bottleneck: under a single-chain architecture, transaction throughput (TPS) remained around 15 transactions per second, while network congestion could cause confirmation delays lasting several hours. To mitigate this issue, the community explored multiple scalability solutions:
- Plasma: Proposed the use of child chains for state computation, submitting only final results to the main chain. This approach resembled “sidechains plus fraud proofs,” significantly reducing the mainnet’s computational load. However, Plasma faced challenges such as complex exit mechanisms and insufficient data availability, preventing it from becoming mainstream.
- State Channels: Enabled high-frequency interactions via off-chain multi-signature agreements, with settlements recorded on-chain only when necessary. While suitable for high-interaction use cases like payments, state channels were constrained by fixed participants and lacked general scalability.
- Sidechains: Operated as independent blockchains interacting with Ethereum through cross-chain bridges, offering flexibility but relying on their own consensus mechanisms. This limited their ability to fully inherit Ethereum’s security guarantees.
During the same period, ERC-20 emerged as the standard for token issuance, providing a unified interface for tokens to interact with wallets and exchanges. Soon after, ERC-721 facilitated the explosive growth of NFTs. These standardization efforts laid the institutional foundation for the flourishing of the Ethereum ecosystem.
4.2 The Upgrade Path: Ethereum 1.x → Ethereum 2.0 (2019–2021)
Between 2019 and 2021, Ethereum entered a critical stage of upgrades and transition. To improve performance and security, the network underwent several hard forks—including Byzantium, Constantinople, and Istanbul—each introducing improvements such as greater virtual machine efficiency, expanded contract functionality, and optimized gas costs. During this time, the community formally proposed the Ethereum 2.0 roadmap, with the goal of achieving higher scalability and energy efficiency through Proof of Stake (PoS) and sharding.
PoS is a blockchain consensus mechanism where nodes secure the network by staking their cryptocurrency to earn the right to propose new blocks. The higher the stake, the greater the chance of selection. Honest validators are rewarded, while malicious ones risk losing their staked funds. Compared to traditional Proof of Work, PoS is more energy-efficient while maintaining network security. Sharding, on the other hand, is a scalability method that partitions the blockchain network into multiple smaller shards, each processing a subset of transactions independently. This allows transactions to be handled in parallel, significantly increasing throughput while reducing the computational and storage burden on individual nodes.
This period also saw the rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), which provided strong momentum for Ethereum’s technical evolution. Projects such as MakerDAO’s DAI stablecoin, Uniswap’s automated market-making model, and Compound’s lending protocol positioned Ethereum as the core infrastructure of decentralized finance. By the end of 2020, the total value locked (TVL) in DeFi on Ethereum had surpassed $15 billion, with daily transaction fees even exceeding those of Bitcoin. The rapid growth in application demand underscored the urgency of the ETH2.0 upgrade.
4.3 Fee Market Reform: The London Upgrade and EIP-1559 (2021)
In 2021, the London hard fork introduced EIP-1559, marking a fundamental reform of Ethereum’s economic model. The proposal replaced the traditional first-price auction with a mechanism where a base fee (the minimum required for inclusion in a block) is burned, while an optional tip compensates miners. The reform aimed to mitigate gas fee volatility, improve user experience, and introduce deflationary pressure into Ethereum’s monetary system.
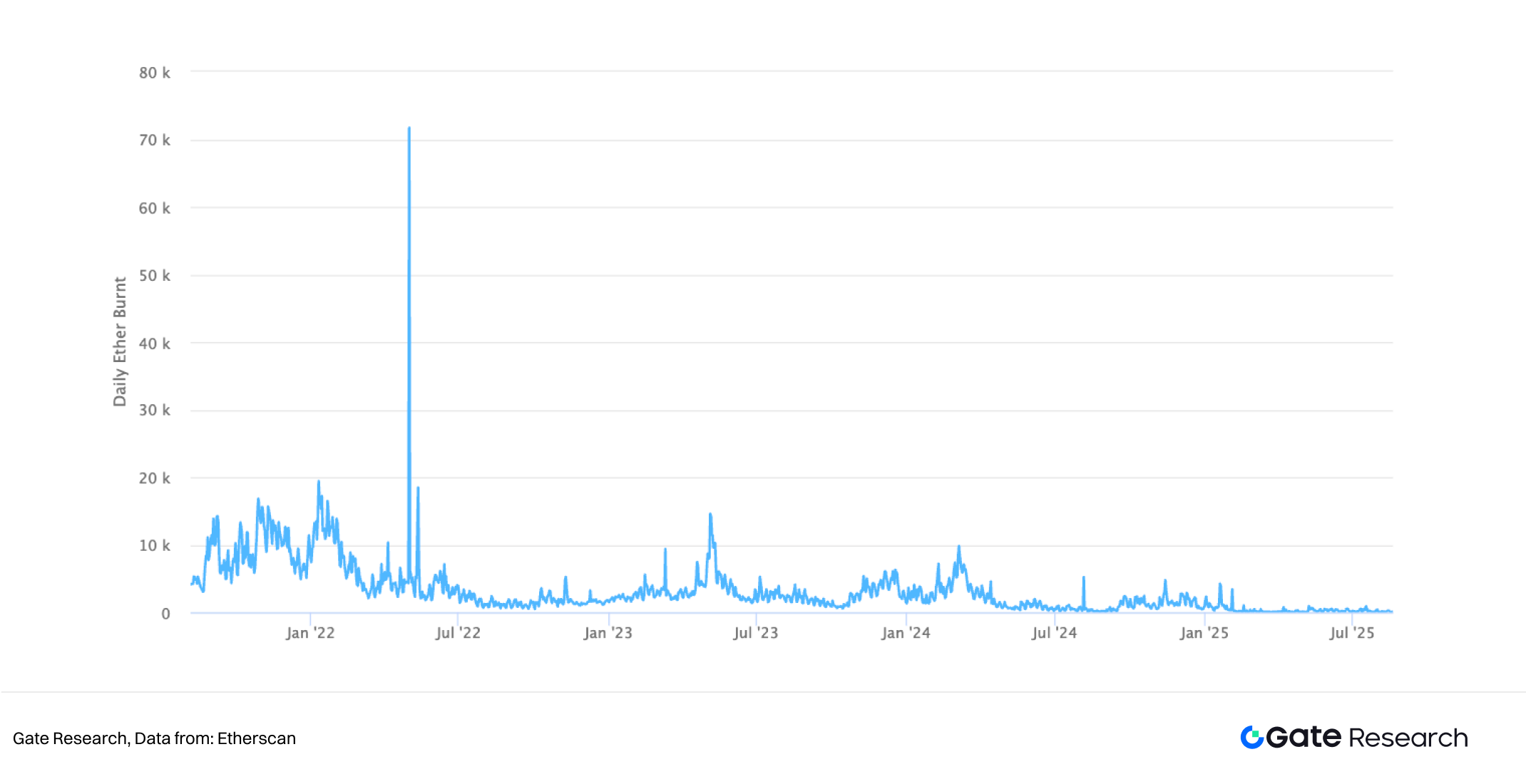
From a data perspective, within one year of EIP-1559’s activation, more than 2 million ETH had been permanently burned—representing tens of billions of dollars in removed supply. This gave ETH an emerging deflationary characteristic, creating a new scarcity narrative distinct from Bitcoin’s fixed-supply model. Meanwhile, miners’ revenue structure shifted to rely more heavily on block rewards and tips, while users experienced significantly reduced fee volatility. EIP-1559 not only optimized the transaction experience but also added a new dimension to ETH’s role as a store of value.
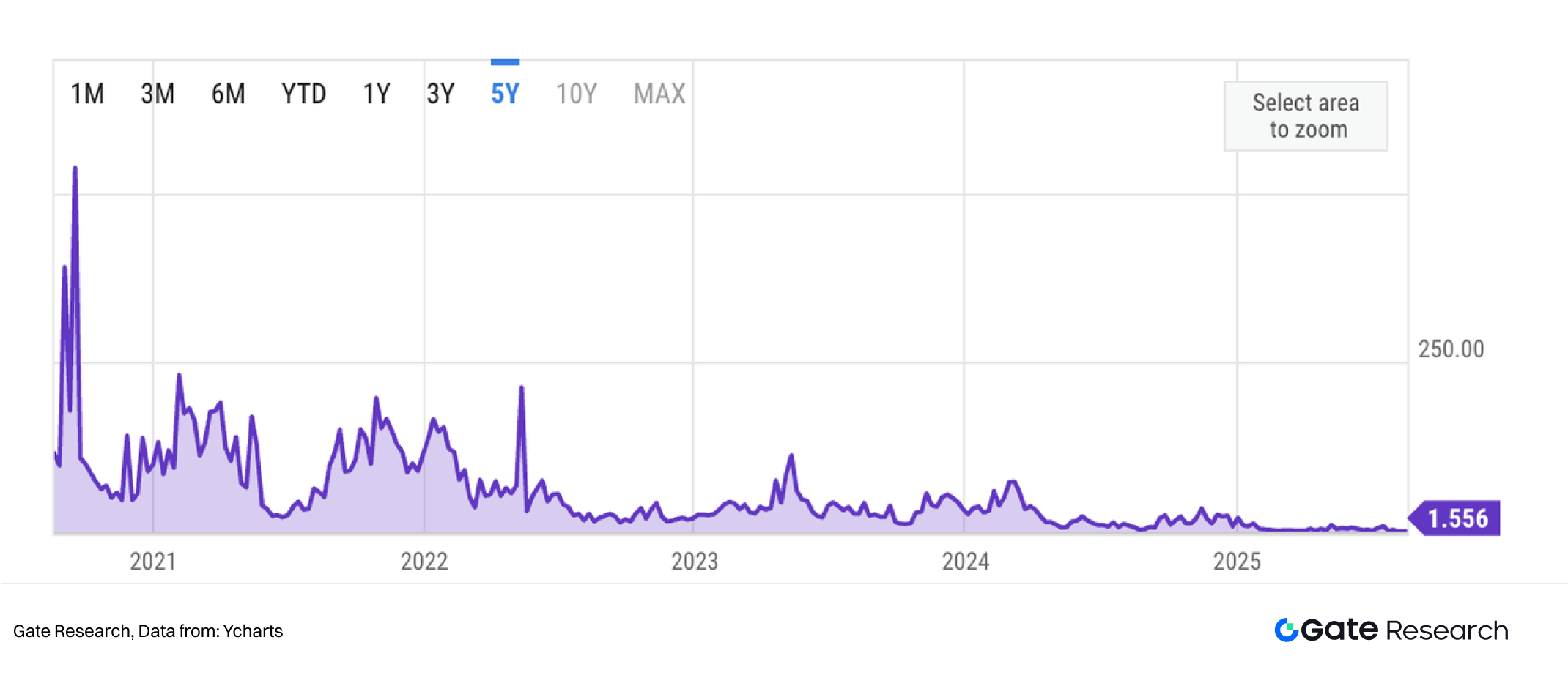
4.4 A Historic Turning Point: The Merge (2022)
In September 2022, Ethereum completed The Merge, a landmark upgrade that transitioned its consensus mechanism from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS). This transition was one of the most technically challenging undertakings in cryptocurrency history, involving years of development and extensive testnet rehearsals.
With The Merge, block production responsibilities shifted from miners to validators. As a result, Ethereum’s energy consumption dropped by more than 99%, dramatically improving its standing in discussions of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations. Beyond energy efficiency, the upgrade also established the foundation for future scaling solutions, reinforcing Ethereum’s position as the leading platform for decentralized applications.
4.5 A New Era of Scalability: Rollups and Data Availability (2023–2025)
From 2023 onward, Ethereum entered a new wave of scalability exploration, with rollups emerging as the dominant path. Both Optimistic Rollups and Zero-Knowledge Rollups (ZK-Rollups) began to coexist and compete across different application scenarios. By offloading most computation off-chain and only submitting data to the mainnet, rollups significantly increased transaction throughput. In 2023, the Total Value Locked (TVL) of Arbitrum and Optimism each surpassed $2 billion, while ZK-based solutions such as zkSync and StarkNet demonstrated strong potential in both performance and security.
In 2024, Ethereum implemented EIP-4844 (Proto-Danksharding), which introduced the “blob” data structure to drastically reduce data costs for rollups, laying the foundation for full Danksharding in the future. This upgrade is regarded as a milestone on Ethereum’s scalability roadmap.
At the same time, the launch of Account Abstraction (EIP-4337) improved wallet usability, enabling features such as gas fee sponsorship, batch transactions, and more flexible permission controls—effectively lowering the entry barrier for new users. On the research frontier, mechanisms such as MEV (Maximal Extractable Value), PBS (Proposer-Builder Separation), and Restaking were proposed to optimize block production, mitigate arbitrage exploitation, and introduce new layers of security and yield within Ethereum.
Overall, the technological evolution between 2023 and 2025 marked Ethereum’s gradual transition from the bottlenecks of a single-chain architecture to a layered design, where the base layer serves as a settlement layer while rollups act as execution layers. This shift is driving Ethereum toward becoming higher-performance, more user-friendly, and more sustainable infrastructure.
Drivers and Patterns of Technological Evolution
Ethereum’s decade-long evolution has not been a mere sequence of functional upgrades, but rather the outcome of interacting internal and external driving forces. These can be summarized into four categories: market demand, technical bottlenecks, community governance and standardization, and external pressures.
- Market demand as the primary driver. The prosperity of ICOs, DeFi, NFTs, stablecoins, and cross-chain assets consistently increased on-chain transaction volume and user demand. For example, the 2017 ICO boom accelerated the adoption of the ERC-20 standard, while the 2020–2021 DeFi surge pushed daily Ethereum transactions beyond 1.5 million and TVL past $150 billion. Such demand pressured the base protocol to continuously optimize throughput, fees, and user experience—or risk being unable to support ecosystem growth.
- Technical bottlenecks as catalysts for innovation. With early throughput capped at ~15 TPS, Ethereum struggled to support large-scale applications. Network congestion and high gas fees became the norm. Events such as the CryptoKitties spike and DeFi fee surges directly prompted the development of Plasma, state channels, and rollups. Nearly every technical upgrade has been born from such “pain points.” For instance, EIP-1559 was proposed in response to gas fee volatility and user experience concerns, introducing base fee burning and a deflationary mechanism.
- Community governance and standardization as key enablers. Through the EIP (Ethereum Improvement Proposal) process, Ethereum established an open and transparent mechanism for shaping its technical roadmap. From ERC-20 to ERC-721, and later EIP-1559 and EIP-4337, each standardization milestone unified ecosystem rules, lowered development barriers, and amplified network effects. The community’s capacity for consensus-building has become a distinctive competitive advantage compared to other blockchains.
- External pressures and shifts in value perception. For instance, environmental concerns over energy consumption accelerated the adoption of Proof of Stake, with The Merge reducing Ethereum’s energy usage by over 99% and improving its ESG profile. Regulatory shifts, investor preferences, and cyclical market dynamics have also influenced protocol design and economic models. Narratives such as ETH’s deflationary nature, staking yields, and rollup adoption can all be interpreted as responses to these external signals.
In summary, Ethereum’s evolution follows several clear patterns:
- A demand–bottleneck–innovation loop: application growth drives network stress, bottlenecks emerge, and in turn, technical innovation arises.
- Standardization first, ecosystem growth follows: early ERC standards paved the way for DeFi, NFTs, and stablecoins.
- Stepwise phased upgrades: from Ethereum 1.x to 2.0, and now to a rollup + sharding architecture, each upgrade balances performance, security, and incentives.
- Economic models co-evolve with technology: reforms in gas fees, ETH burning, and PoS staking illustrate how technical upgrades are closely intertwined with value capture mechanisms.
Industry Impact Analysis
Looking back on Ethereum’s ten-year trajectory, its technological evolution shows a clear trend: from a single-chain smart contract platform toward a multi-layered, high-performance, economically optimized, and user-friendly ecosystem. Between 2015 and 2025, Ethereum went through several critical phases—early ecosystem building (ERC standardization, ICO boom), scalability explorations (Plasma, state channels), economic model innovations (EIP-1559 and its deflationary mechanism), historic protocol upgrades (The Merge), and the rise of rollup and sharding technologies. Each phase was closely tied to application demand, network stress, and community governance.
From a data perspective, Ethereum’s active address count grew from several hundred thousand in 2016 to more than 200 million by 2025, while peak daily transaction volume exceeded 2 million. In 2023, DeFi total value locked (TVL) reached an all-time high of over $105.6 billion. These indicators reflect not only the prosperity of the Ethereum ecosystem but also the persistent pressure on its base-layer technology to deliver scalability, efficiency, and improved user experience.
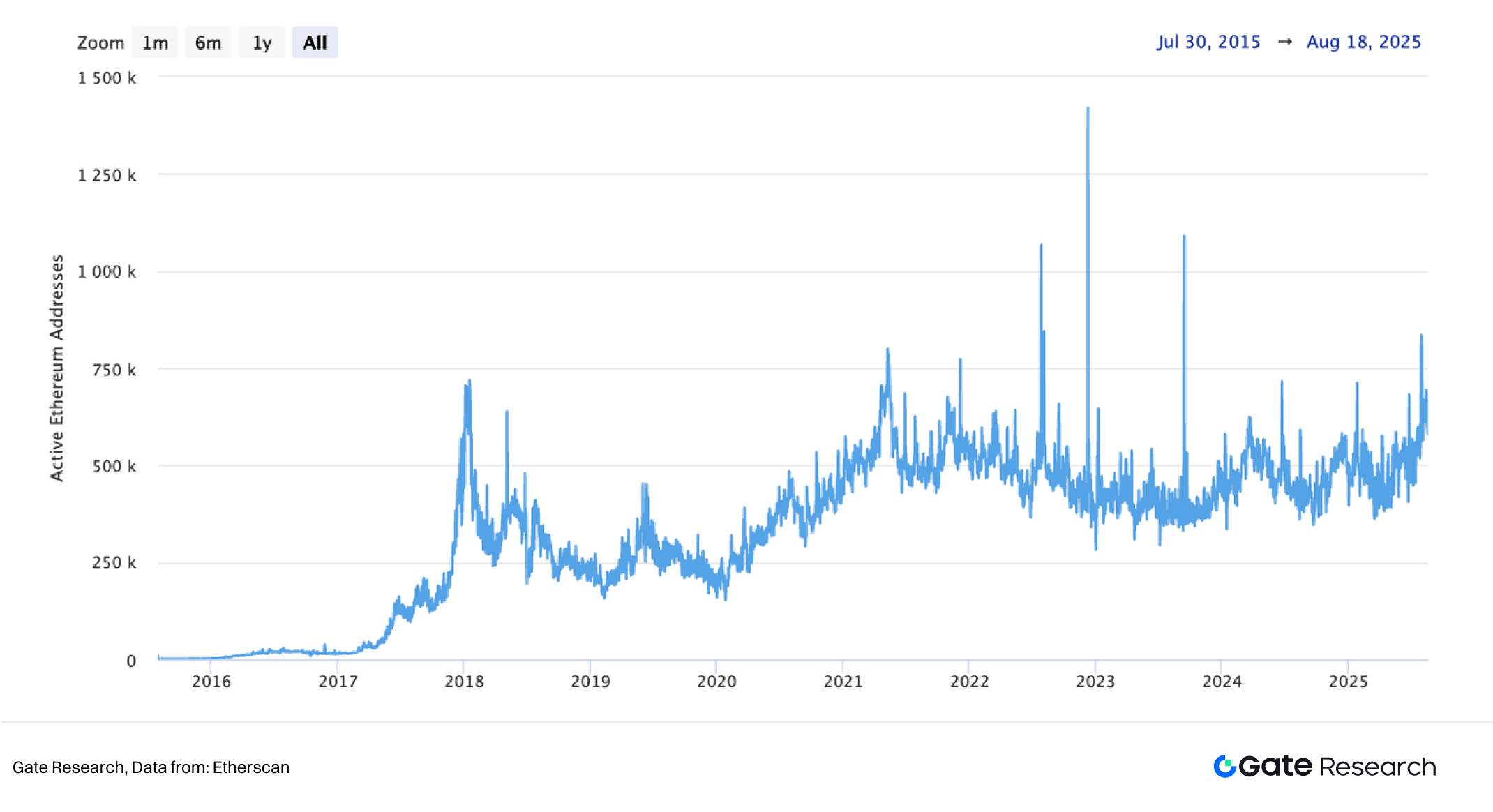
Looking ahead, several trends are likely to shape Ethereum’s future:
- Deployment of Multi-Layer Scalability Architectures. Rollups have become the mainstream scaling solution, while the implementation of Proto-Danksharding has paved the way toward full sharding. In the coming years, Ethereum is expected to achieve efficient coordination between rollup execution layers and sharded data layers, increasing throughput from dozens of transactions per second to tens of thousands, while significantly reducing transaction costs.
- User Experience and Account Abstraction Optimization. Mechanisms such as EIP-4337 have lowered the barriers for new users. Future developments may include more flexible gas fee sponsorship, batch transactions, and cross-application account management—bringing Web3 usability closer to that of traditional internet applications.
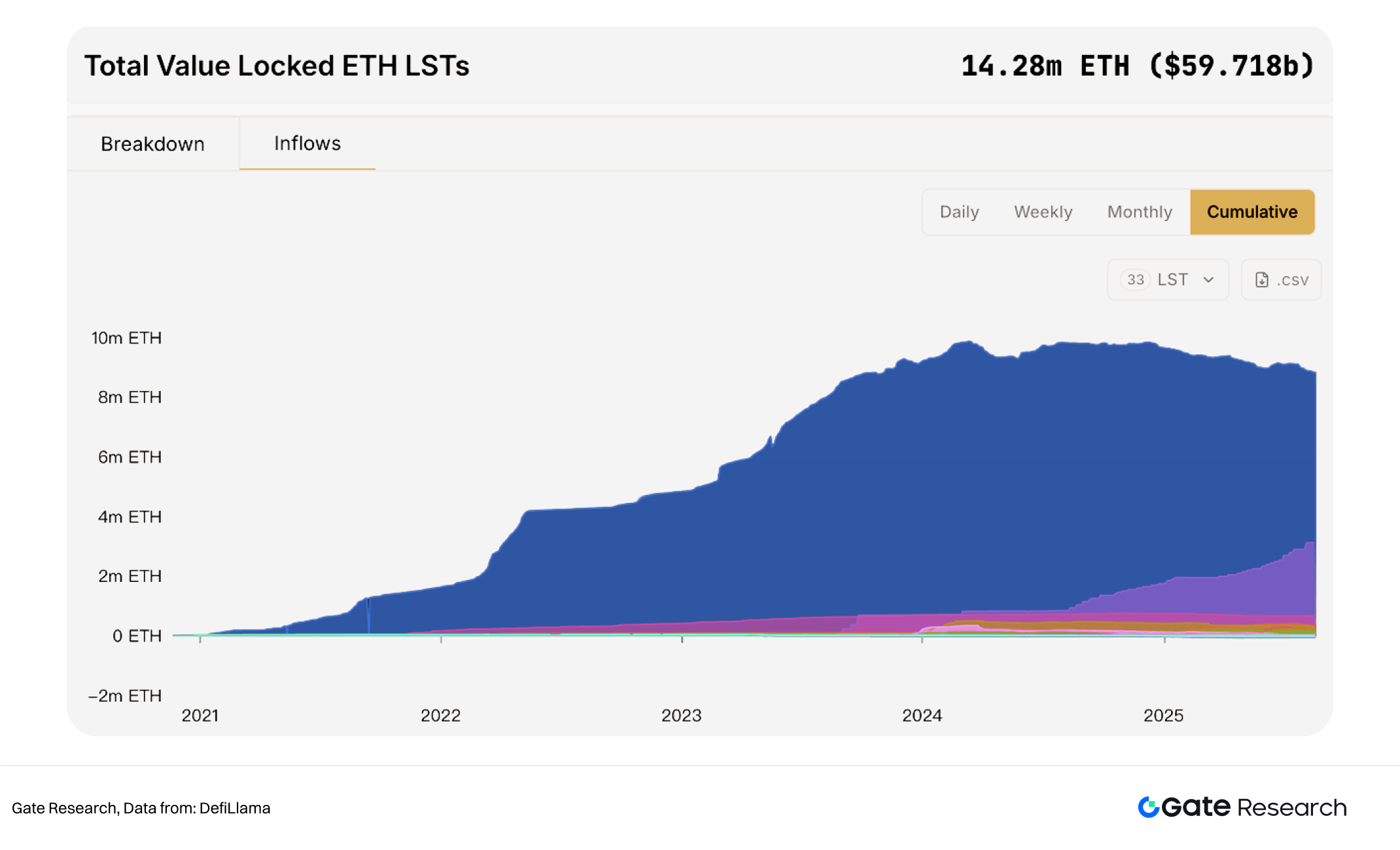
- Evolution of Economic Models and Incentive Mechanisms. As PoS staking matures, ETH’s deflationary profile, liquid staking, and MEV governance will continue to shape network security and yield structures. Innovations like restaking may create new layers of value capture, offering richer incentives for validators and protocols alike.
- Sustainability and Governance as Core Competitiveness. ESG considerations, energy efficiency, transparency of on-chain governance, and community consensus mechanisms will directly influence Ethereum’s position in the multi-chain competitive landscape. Through technical upgrades and economic model refinements, Ethereum is well positioned to maintain its leading role in the global blockchain ecosystem, while supporting Web3 finance, DAOs, and cross-chain interoperability.
Future Outlook
Despite Ethereum’s remarkable technical breakthroughs and ecosystem expansion over the past decade, its development still faces a range of challenges and risks—spanning technical, economic, regulatory, and competitive dimensions.
- Scalability and performance uncertainties. Although rollups and sharding offer theoretical improvements in throughput, real-world deployment still faces challenges such as data availability, cross-rollup latency, and protocol complexity. For example, Optimistic Rollups rely on fraud proofs, which impose withdrawal delays of up to a week, while ZK-Rollups still face high computational costs for generating zero-knowledge proofs. Rapid or uncoordinated rollup growth could lead to inconsistent user experiences or even renewed congestion.
- Economic incentives and security risks. While PoS significantly reduces energy consumption, validator incentive structures must balance security with yield. Currently, over 16 million ETH—more than 13% of circulating supply—is staked. If concentrated in a few large staking providers, centralization risks could emerge. Meanwhile, MEV (Maximal Extractable Value) remains unresolved, as arbitrage-driven transaction ordering may distort fairness and threaten network integrity.
- Protocol complexity and upgrade risks. Ethereum’s transition from a single-chain design to a multi-layer rollup + sharding architecture has increased systemic complexity. Each upgrade—whether The Merge, EIP-4844, or future full sharding—carries risks of implementation errors, contract incompatibilities, and delayed node updates. Past incidents of chain desynchronization and bugs during forks underscore the need for extreme caution in large-scale upgrades.
- Regulatory and legal pressures. With the rapid rise of DeFi, stablecoins, and NFTs, global regulators are paying closer attention to on-chain financial activities. Future compliance requirements may constrain Ethereum’s decentralization and raise operational costs for developers and users. In particular, regulation of cross-chain transactions and staking derivatives introduces uncertainty that could directly impact liquidity and participation.
- Ecosystem competition and cross-chain challenges. Emerging blockchains such as Solana, Polkadot, and Avalanche attract users and developers with higher throughput and lower fees. If Ethereum’s rollup-centric scaling strategy progresses too slowly, it risks losing market share. Moreover, secure and efficient cross-chain interoperability remains unsolved; without it, Ethereum’s role in a multi-chain Web3 ecosystem could be constrained.
In sum, Ethereum’s future risks cluster around scalability, economic incentives, protocol complexity, regulatory uncertainty, and ecosystem competition. Sustaining long-term growth will require the community, developers, and investors to strike a balance between continuous innovation and operational resilience—pursuing performance and scalability improvements while safeguarding against security, compliance, and centralization risks.
Reference
- Ethereum, https://ethereum.org/zh/history/
- Ethereum, https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-1559
- Ethereum, https://etherscan.io/chart/dailyethburnt
- Defillama, https://defillama.com/lst
Gate Research
Gate Research is a comprehensive research platform focused on blockchain and cryptocurrency. It provides in-depth content covering technical analysis, market trends, sector research, macroeconomic insights, and policy developments.
Click here to explore
Disclaimer
Investing in the cryptocurrency market involves high risk. Users are advised to conduct independent research and fully understand the nature of the assets and products before making any investment decisions. Gate.io is not liable for any losses or damages resulting from such investment activities.
Related Articles

Gate Research: BTC Breaks $100K Milestone, November Crypto Trading Volume Exceeds $10 Trillion For First Time

Gate Research: 2024 Cryptocurrency Market Review and 2025 Trend Forecast

Detailed Analysis of the FIT21 "Financial Innovation and Technology for the 21st Century Act"

Gate Research-A Study on the Correlation Between Memecoin and Bitcoin Prices

Gate Research: Web3 Industry Funding Report - November 2024
